Surely you’ve ever wondered how Netflix can go ahead and suggest you watch series that you end up loving. Or how Instagram makes your feed show you everything you like, which is different when you compare it with your friends.
This is thanks to artificial intelligence, machine learning, LLM… buzzwords that are on everyone’s lips, but what exactly do they mean?
Eilder Jorge, Head of Data Department
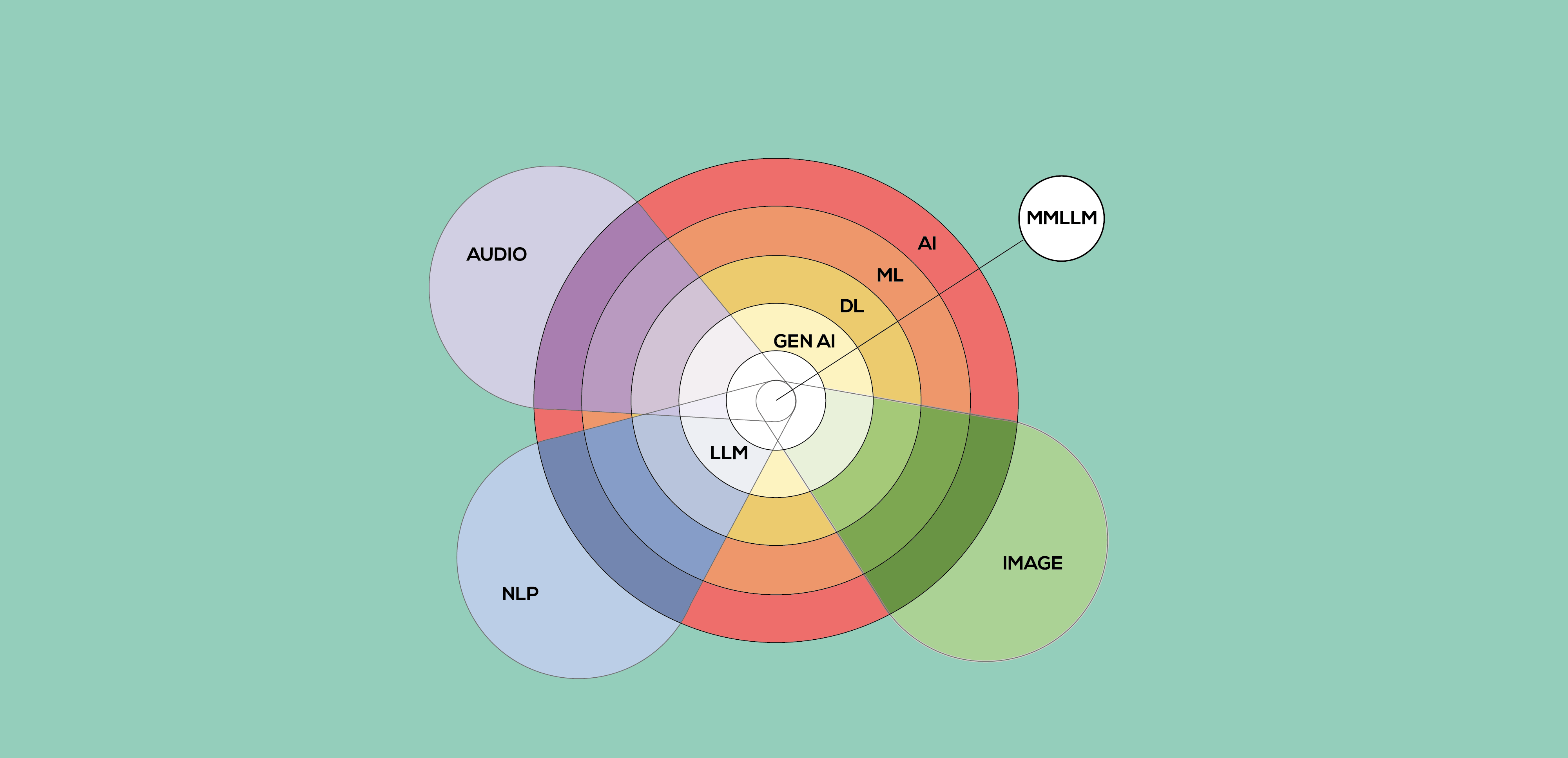
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):It is the ability of machines to emulate human intelligence, enabling them to perform tasks such as reasoning, problem solving, learning, perceiving the environment and making decisions. It encompasses techniques such as machine learning, robotics, expert systems and natural language processing. An example of this is the use of AI for the optimisation of intralogistics in industrial plants with AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) from our RobotVec project.
- Machine Learning (ML): An area of AI that focuses on the use of algorithms and statistical models to enable systems to learn from data without being explicitly programmed. It is classified into three types: supervised learning (with labelled data), unsupervised learning (where patterns are identified in unlabelled data) and reinforcement learning (based on feedback). At WonderBits, for example, we use ML for vehicle repair estimation for a digital appraisal platform we developed.
- Deep Learning (DL): A sub-discipline of machine learning that simulates the functioning of neural networks in the brain. DL models automatically detect patterns in data and are particularly effective in tasks such as image or speech recognition, although they require large amounts of data and computational resources.
- Generative Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI): This refers to a type of AI technology that creates new content, such as text, images, audio, video or even code, from the data it has been trained on. Instead of just recognising patterns or analysing data, generative AI can produce original results. An example of this is the famous ChatGPT.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): It is a field of AI that allows machines to understand, interpret and generate human language in a coherent and contextual way. Any application related to text and language analysis in the field of deep learning belongs to the NLP area. An example of this would be the analysis of a company’s customer reviews to understand the degree of satisfaction with the service.
- Large Language Model (LLM): An LLM is based on human language generation, and is the evolution of the language model concept in artificial intelligence, which dramatically expands the data used for training and inference. This, in turn, provides a massive increase in the capabilities of the AI model. Although there is no universally accepted figure for the size of the dataset needed for training, an LLM generally has at least a billion (or more) parameters. Parameters are a machine learning term that refers to the variables present in the model on which it was trained and which are used to infer new content. The creation of intelligent virtual assistants to provide technical assistance in machinery maintenance via voice queries would be an example of an LLM application.
- Multi Modal Large Language Model (MMLLM): A multimodal LLM can handle and integrate different types of inputs (e.g. process text together with images) and generate outputs in these different modes. For example, it could generate descriptions of images, provide textual responses based on visual inputs, or interpret diagrams together with written explanations. In practice, these models can perform tasks such as generating captions for images, answering visual questions or working with multimedia content.
Would you like to implement artificial intelligence in your company in order to optimize processes and make data-driven business decisions? Write to us at hello@wonderbits.net!